In a remarkable breakthrough, researchers at Germany’s esteemed Aerospace Center have redefined the realm of robotic sensation by merging traditional force-torque sensors with sophisticated machine-learning algorithms. This pioneering research, showcased in the journal Science Robotics, unveils a refreshing alternative to the traditional reliance on artificial skin for endowing robots with a sense of touch. By addressing touch as a bidirectional experience—where not only do we perceive our environment, but we also respond to it—this study opens new corridors in robotic functionality.
Rethinking Touch in Robotics
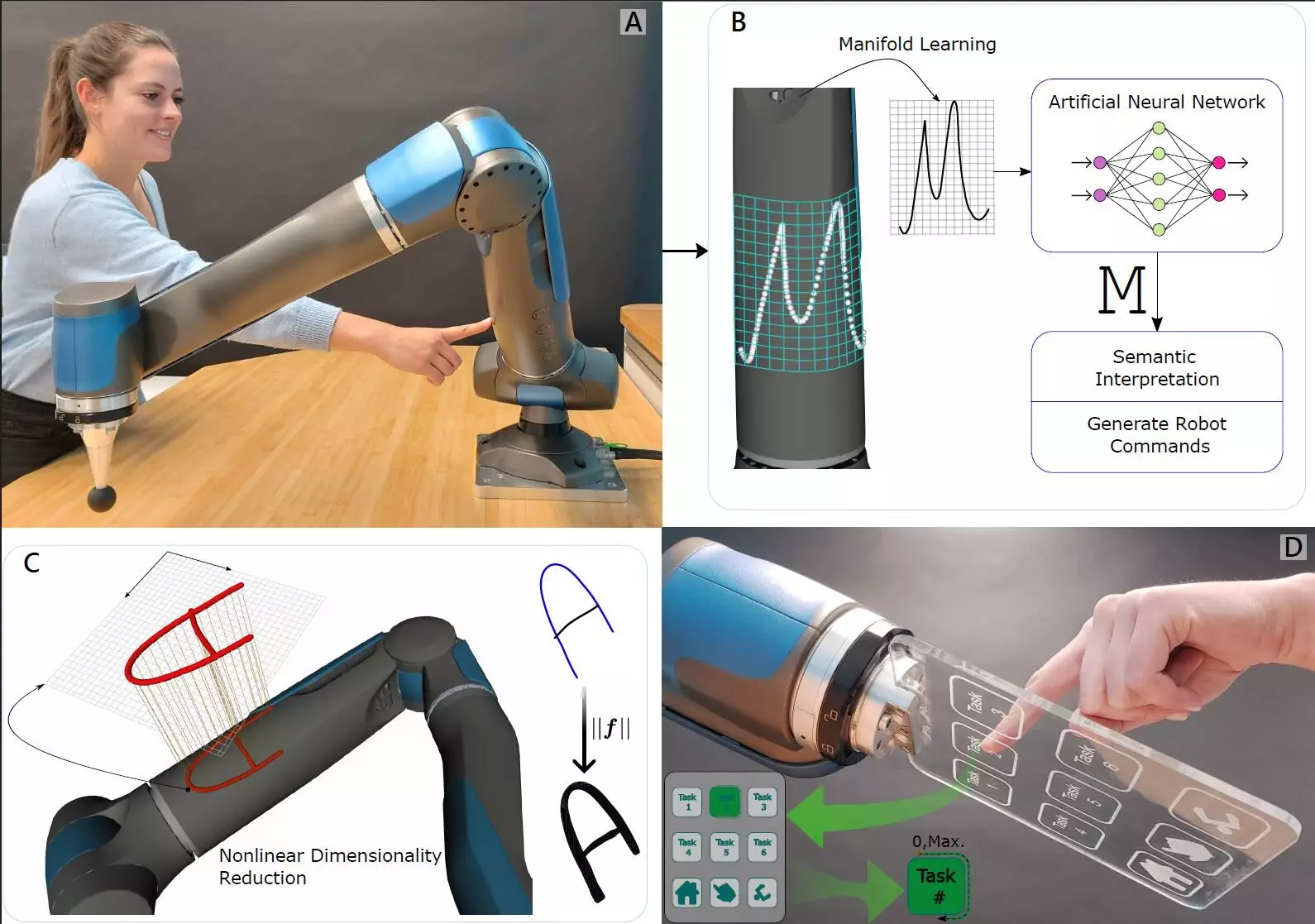
The team’s innovative strategy emphasizes the importance of torque as a pivotal aspect of touch. Living beings recognize sensations through intricate feedback mechanisms; similarly, the researchers implanted highly sensitive force-torque sensors into the joints of a robotic arm. Through this design, the robot can capture not just the pressure exerted upon it but also recognize varying intensities and directions of that pressure. This nuanced communication of force transforms the robot’s ability to interpret touch from simple pressure detection to a rich narrative of sensory experience.
The Role of Machine Learning
Harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, the roboticists deployed a machine-learning algorithm to make sense of the data collected from these sensors. By training the system to identify different tension patterns, the robots can distinguish among diverse touch situations. For instance, they can pinpoint where they are being touched and even discern what number is being pressed against them. This capability goes beyond basic reactions; it allows for a nuanced interaction that could be essential for collaborative tasks in industrial settings where human workers share space with robotic counterparts.
Practical Implications for Human-Robot Interaction
This enhanced understanding of touch could revolutionize the way we perceive and interact with robots in various applications. In industrial environments, where precision and safety are paramount, a robot that can intuitively sense and respond to human touch could dramatically enhance collaborative processes. Robots equipped with this advanced perception system can adjust their actions more accurately, thereby minimizing physical risks during interactions with humans. Additionally, such advancements could lead to wider acceptance of robots in everyday scenarios, fostering a future where they are integral to various domains, from healthcare to hospitality.
A Leap Beyond Conventional Robotics
The implications of this research extend far beyond immediate industrial applications. By immersing traditional robotics in an experiential learning methodology, the findings challenge the very fabric of how we envision human-robot relationships. As machines gain the capability to sense touch more like humans, the potential for empathy and understanding between humans and robots can fundamentally shift, encouraging collaboration rather than mere servitude. This research might pave the way for a hybridized future where robots not only assist but also engage meaningfully with their human counterparts.
In essence, the innovative strides made by this research team herald a new era of robotic touch perception—a game-changer with expansive possibilities for human-robot interaction. As we step into this new territory, the ever-blurring lines between technology and human experience become increasingly fascinating.